Product Description
How to extend the lifetime of the cv joint/drive shaft/axle shaft/half shaft universal joint?
1.Regularly check the cv joint/drive shaft/axle shaft/half shaft sheath
Since the cv joint boot/drive shaft/axle shaft/half shaft is an important part to protect the life of the cv joint, the quality of the cv joint boot is the key. Usually we have a good habit of keeping a car and checking the vehicle. It is necessary to check the status of the vehicle before driving every day. Check the cv joint/drive shaft/axle shaft/half shaft jacket for oil leakage every week.
2. Avoid prolonged wading
If you drive in water deeper than the position of the cv joint for a long time, it is easy to cause water to enter the inside of the cv joint.
3. Regular cv joint maintenance
If you want to prolong the life of the cv joint/drive shaft/axle shaft/half shaft, regular maintenance is necessary. If the dust cover boot is not damaged, we can clean and refill the cv joint every 4 years or 60, 2 2 1
Reference our cv joint packing way,we have full experience to supply different brands all over the world:
Our HDAG CV JOINTS universal joint Drive shafts machining and production workshops:
Our HDAG CV JOINTS universal joint Drive shafts assemble line:
Our semi finished CV JOINT universal joint Drive shaft in stock before packing and shipment:
HDAG CV JOINTS universal joint Drive shafts pull push force and tensile testing, assemble Testing, full size tolerance testing:
I. We only do OEM, produce high precisional Auto CV JOINT,Universal Joint,Car CV JOINT INNER OUTER, DRIVE SHAFT, DRIVESHAFT,CV AXLE, JOINT SHAFT ASSEMBLY,CV AXLE JOINT SHAFT, HALF SHAFT, WHEEL BEARING HUB, WHEEL HUB BEARING, WHEEL BEARING, different with other factories
II.Quality guarantee: We promise to all of our old and new customers: ONE year guarantee or 50,E 1H0498099A/1H57111/357498099EX/357498099EV/357498099E/1J57111D
CZPT :
CZPT :
CZPT :
CZPT : 4342
CZPT : 4342
CZPT : 4342R20
CZPT : 4346R30
CZPT : 4346S50
CZPT : 4346
CZPT : 4347S60
CZPT : 4347U90
CZPT :
CZPT :
CZPT : 434708Z033
CZPT : 434708Z037
CZPT : 391571JJ10
CZPT : 39157117JJ10
CZPT : 3910110JJ10
CZPT : 391Y10
CZPT : 391M570
CZPT : 391N215
CZPT : 391571M311
CZPT : 391571M915
CZPT : 3910140Y10
CZPT : 391014M570
CZPT : 391014M575
CZPT : 391014M771
CZPT : 3910163Y10
CZPT : 391016N215
391012Y175
392112Y070
391J210
CZPT : 391J171
CZPT : 391N275
CZPT : 391J071
CZPT : 391J915
CZPT : 391E478
CZPT : 391012J215
CZPT : 391014N175
CZPT : 391014N177
CZPT : 391014N275
CZPT : 391015J571
CZPT : 391016J571
CZPT : 391016J071
CZPT : 391016J076
CZPT : 391016J915
CZPT : 39101AE415
CZPT : 39101AU415
CZPT : 39101AU416
CZPT : 39101AW110
CZPT : 39101CX116
CZPT : 39101WF715
CZPT : 39101WF716
3921185E
CZPT : 4347Z035
CZPT : 434708Z039
191498103A
191498103C
191498103CV
191498103CX
191498104C
321498103D
357498103
357498103A
357498103V
357498103X
357498350X
191498103
1K0498103
VAG :
,96396134,512395
CZPT : 391V70A
CZPT : 391013U505
CZPT : 391014V01C
CZPT : 391014V51A
CZPT : 391014V70A
CZPT : 392113U
96348790
CZPT : 8111304
CZPT : 86011
CZPT : 9122833
CZPT : 9163595
MAZDA : G571550X
MAZDA : G571560X
MAZDA : G565715
OPEL : 374
VAUXHALL : 571
391
MAZDA : MD1922510
MAZDA : MD1922510A
MAZDA : MD192550X
MAZDA : MD257160XB
33
A
OPEL : 374048
OPEL : 374067
OPEL : 37408
OPEL : 374118
OPEL : 374148
OPEL : 374195
OPEL : 90125876
OPEL : 90157212
OPEL : 95718734
OPEL : 9317340
OPEL : 93173430
SAAB : 4242319
A1683601872
CZPT : 391KD0A
CZPT : 391019Y015
CZPT : 39101CNY015
CZPT : 39211CN,7701349689,7701349839,7701349873
,7701351948,7701352571,7701352571
,7701498918,7701498919,7701498921
3910173N10
HONDA : 44305S04J60
HONDA : 44305S0A960
HONDA : 44305S0AN60
HONDA : 44305S2H571
HONDA : 44305S2H050
HONDA : 44305S2H950
HONDA : 44305S2H951
HONDA : 44305S2HN50
HONDA : 44305S5AJ50
HONDA : 44305S5AJ60
HONDA : 44305S5AJ61
HONDA : 44305S5AJ62
HONDA : 44305S5C950
HONDA : 44305S5CN50
HONDA : 44305S5CN51
HONDA : 44305S7B950
HONDA : 44305S7C950
HONDA : 44305SOA960
HONDA : 44305SOAN60
HONDA : 44306S0A960
HONDA : 44306S0AN60
HONDA : 44306S2H571
HONDA : 44306S2H950
HONDA : 44306S2H951
HONDA : 44306S5AJ51
HONDA : 44306S5AJ61
HONDA : 44306S5AJ62
HONDA : 44306S5C951
HONDA : 44306S5C952
HONDA : 44306S7B950
HONDA : 44306S7C950
HONDA : 44306SOA960
HONDA : 44306SOAN60
326582
FG02-25-500E
FG02-25-600D
FG02-25-600E
44305-SA2-960
39100ED00A
39101ED00A
39101ED005
44571-SH3-J01,44306-SB2-984
39211-CN000
CZPT : 0K558-25-60X
3272.S5
39211-AY125
39101-AX005
39100-AX005
39101-AX000
MAZDA : M 0571 1510A
MAZDA : M 0571 1500C
MAZDA : M 0571 1500D
MAZDA : M 0571 1600A
MAZDA : M 0571 1600B
MAZDA : MD0925500A
MAZDA : MD0925600A
MAZDA : G064-25-600
MAZDA : G564-25-500A
MAZDA : G564-25-600A
MAZDA : G564-25-60X
MAZDA : GR01-25-500
MAZDA : GR01-25-50X
MAZDA : GR01-25-600
MAZDA : GR01-25-60X
MAZDA : GU01-25-500
MAZDA : GU01-25-50XA
MAZDA : GU01-25-50XC
MAZDA : GU01-25-600
MAZDA : GU01-25-60XA
MAZDA : GU01-25-60XD
HONDA : 44014-SNG-000
HONDA : 44305-SDC-A00
HONDA : 44305-SEA-000
HONDA : 44305-SNG-571
HONDA : 44306-SDC-A01
HONDA : 44306-SDE-T00
HONDA : 44306-SEA-000
HONDA : 44306-SNG-571
CZPT : 39100JD24B
CZPT : 39100JD52B
CZPT : 39101JD24B
CZPT : 39101JD52B
CZPT : 39211JA00A
CZPT : 39211JD22B
CZPT : C9211JA00A
CZPT : C9211JD22B
CZPT : C92AAJA00A
CZPT : C92AAJD22B
CZPT : C9B11JA00A
CZPT : C9BAAJA00A
MAZDA : FA8571500A
MAZDA : FA8571600B
MAZDA : FA8125600B
MAZDA : FA8225500A
MAZDA : FD8571500B
MAZDA : FD8571600A
MAZDA : FP0125500C
3272-HY
3272-KW
3273-HQ
3273-KJ
CZPT : 39100-ED105
CZPT : 39100-ED305
CZPT : 39100-ED805
CZPT : 39101-ED105
CZPT : 39101-ED305
CZPT : 39101-ED805
CZPT : 39211-ED100
CZPT : C9211-EL10A
CZPT : KK38825600
CZPT : 49500-25302
CZPT : 49500-25310
CZPT : 49500-25311
CZPT : 49500-25312
CZPT : 49500-25301
CZPT : 49500-25302
CZPT : 49500-25310
CZPT : 49500-25311
CZPT : 49500-25312
LAND ROVER : STC3046
40011-M5626
39100-M7270
39101-M7270
39113-M7275
39112-M7225
LAND ROVER : TDJ00571
CZPT : 49500-25400
CZPT : 49500-25200
CZPT : 49500-25400
LAND ROVER : TDB500110
LAND ROVER : TDJ500030
39101-CA100
39211-CA100
39100-CA100
HONDA : 44305S74E01
HONDA : 44305S74E51
ROVER : GCV1123
ROVER : TFB000070
39211-AY125
39101-AX005
39100-AX005
39101-AX000
CITROEN : 3272TH
CITROEN : 3272WX
CITROEN : 3273QQ
CITROEN : 3273TT
CITROEN : 3273XR
DS : 3272QF
DS : 3272TH
DS : 3273QQ
DS : 3273TT
PEUGEOT : 3272QF
PEUGEOT : 3272TH
PEUGEOT : 3272WX
PEUGEOT : 3273QQ
PEUGEOT : 3273TT
PEUGEOT : 3273XR
39211-CG571
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Three Years |
|---|---|
| Condition: | New |
| Color: | OEM Standard |
| Certification: | CE, ISO, ISO/Ts16949 |
| Type: | Universal Joint |
| Application Brand: | Nissan, Iveco, Toyota, Ford, Lada Mitsubishi FIAT Opel Peugeot Renault Citroen |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
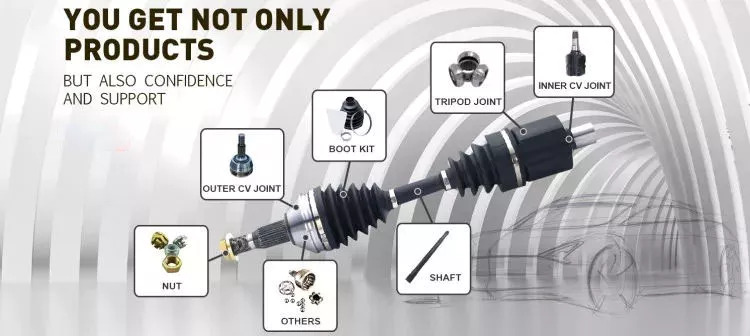
How do drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance?
Drive shafts employ various mechanisms to ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance. Efficient power transfer refers to the ability of the drive shaft to transmit rotational power from the source (such as an engine) to the driven components (such as wheels or machinery) with minimal energy loss. Balancing, on the other hand, involves minimizing vibrations and eliminating any uneven distribution of mass that can cause disturbances during operation. Here’s an explanation of how drive shafts achieve both efficient power transfer and balance:
1. Material Selection:
The material selection for drive shafts is crucial for maintaining balance and ensuring efficient power transfer. Drive shafts are commonly made from materials such as steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their strength, stiffness, and durability. These materials have excellent dimensional stability and can withstand the torque loads encountered during operation. By using high-quality materials, drive shafts can minimize deformation, flexing, and imbalances that could compromise power transmission and generate vibrations.
2. Design Considerations:
The design of the drive shaft plays a significant role in both power transfer efficiency and balance. Drive shafts are engineered to have appropriate dimensions, including diameter and wall thickness, to handle the anticipated torque loads without excessive deflection or vibration. The design also considers factors such as the length of the drive shaft, the number and type of joints (such as universal joints or constant velocity joints), and the use of balancing weights. By carefully designing the drive shaft, manufacturers can achieve optimal power transfer efficiency while minimizing the potential for imbalance-induced vibrations.
3. Balancing Techniques:
Balance is crucial for drive shafts as any imbalance can cause vibrations, noise, and accelerated wear. To maintain balance, drive shafts undergo various balancing techniques during the manufacturing process. Static and dynamic balancing methods are employed to ensure that the mass distribution along the drive shaft is uniform. Static balancing involves adding counterweights at specific locations to offset any weight imbalances. Dynamic balancing is performed by spinning the drive shaft at high speeds and measuring any vibrations. If imbalances are detected, additional adjustments are made to achieve a balanced state. These balancing techniques help minimize vibrations and ensure smooth operation of the drive shaft.
4. Universal Joints and Constant Velocity Joints:
Drive shafts often incorporate universal joints (U-joints) or constant velocity (CV) joints to accommodate misalignment and maintain balance during operation. U-joints are flexible joints that allow for angular movement between shafts. They are typically used in applications where the drive shaft operates at varying angles. CV joints, on the other hand, are designed to maintain a constant velocity of rotation and are commonly used in front-wheel-drive vehicles. By incorporating these joints, drive shafts can compensate for misalignment, reduce stress on the shaft, and minimize vibrations that can negatively impact power transfer efficiency and balance.
5. Maintenance and Inspection:
Regular maintenance and inspection of drive shafts are essential for ensuring efficient power transfer and balance. Periodic checks for wear, damage, or misalignment can help identify any issues that may affect the drive shaft’s performance. Lubrication of the joints and proper tightening of fasteners are also critical for maintaining optimal operation. By adhering to recommended maintenance procedures, any imbalances or inefficiencies can be addressed promptly, ensuring continued efficient power transfer and balance.
In summary, drive shafts ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining balance through careful material selection, thoughtful design considerations, balancing techniques, and the incorporation of flexible joints. By optimizing these factors, drive shafts can transmit rotational power smoothly and reliably, minimizing energy losses and vibrations that can impact performance and longevity.

Can you provide real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that use drive shafts?
Drive shafts are widely used in various vehicles and machinery to transmit power from the engine or power source to the wheels or driven components. Here are some real-world examples of vehicles and machinery that utilize drive shafts:
1. Automobiles:
Drive shafts are commonly found in automobiles, especially those with rear-wheel drive or four-wheel drive systems. In these vehicles, the drive shaft transfers power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential or front differential, respectively. This allows the engine’s power to be distributed to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward.
2. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drive shafts are essential components in trucks and commercial vehicles. They are used to transfer power from the transmission or transfer case to the rear axle or multiple axles in the case of heavy-duty trucks. Drive shafts in commercial vehicles are designed to handle higher torque loads and are often larger and more robust than those used in passenger cars.
3. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
Various types of construction and earthmoving equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and graders, rely on drive shafts for power transmission. These machines typically have complex drivetrain systems that use drive shafts to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks, enabling them to perform heavy-duty tasks on construction sites or in mining operations.
4. Agricultural Machinery:
Agricultural machinery, including tractors, combines, and harvesters, utilize drive shafts to transmit power from the engine to the wheels or driven components. Drive shafts in agricultural machinery are often subjected to demanding conditions and may have additional features such as telescopic sections to accommodate variable distances between components.
5. Industrial Machinery:
Industrial machinery, such as manufacturing equipment, generators, pumps, and compressors, often incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. These drive shafts transfer power from electric motors, engines, or other power sources to various driven components, enabling the machinery to perform specific tasks in industrial settings.
6. Marine Vessels:
In marine applications, drive shafts are commonly used to transmit power from the engine to the propeller in boats, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drive shafts are typically longer and designed to withstand the unique challenges posed by water environments, including corrosion resistance and appropriate sealing mechanisms.
7. Recreational Vehicles (RVs) and Motorhomes:
RVs and motorhomes often employ drive shafts as part of their drivetrain systems. These drive shafts transfer power from the transmission to the rear axle, allowing the vehicle to move and providing propulsion. Drive shafts in RVs may have additional features such as dampers or vibration-reducing components to enhance comfort during travel.
8. Off-Road and Racing Vehicles:
Off-road vehicles, such as SUVs, trucks, and all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), as well as racing vehicles, frequently utilize drive shafts. These drive shafts are designed to withstand the rigors of off-road conditions or high-performance racing, transmitting power efficiently to the wheels and ensuring optimal traction and performance.
9. Railway Rolling Stock:
In railway systems, drive shafts are employed in locomotives and some types of rolling stock. They transfer power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or propulsion system, enabling the train to move along the tracks. Railway drive shafts are typically much longer and may have additional features to accommodate the articulated or flexible nature of some train configurations.
10. Wind Turbines:
Large-scale wind turbines used for generating electricity incorporate drive shafts in their power transmission systems. The drive shafts transfer rotational energy from the turbine’s blades to the generator, where it is converted into electrical power. Drive shafts in wind turbines are designed to handle the significant torque and rotational forces generated by the wind.
These examples demonstrate the broad range of vehicles and machinery that rely on drive shafts for efficient power transmission and propulsion. Drive shafts are essential components in various industries, enabling the transfer of power from the source to the driven components, ultimately facilitating movement, operation, or the performance of specific tasks.

Are there variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery?
Yes, there are variations in drive shaft designs to cater to the specific requirements of different types of machinery. The design of a drive shaft is influenced by factors such as the application, power transmission needs, space limitations, operating conditions, and the type of driven components. Here’s an explanation of how drive shaft designs can vary for different types of machinery:
1. Automotive Applications:
In the automotive industry, drive shaft designs can vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Rear-wheel-drive vehicles typically use a single-piece or two-piece drive shaft, which connects the transmission or transfer case to the rear differential. Front-wheel-drive vehicles often use a different design, employing a drive shaft that combines with the constant velocity (CV) joints to transmit power to the front wheels. All-wheel-drive vehicles may have multiple drive shafts to distribute power to all wheels. The length, diameter, material, and joint types can differ based on the vehicle’s layout and torque requirements.
2. Industrial Machinery:
Drive shaft designs for industrial machinery depend on the specific application and power transmission requirements. In manufacturing machinery, such as conveyors, presses, and rotating equipment, drive shafts are designed to transfer power efficiently within the machine. They may incorporate flexible joints or use a splined or keyed connection to accommodate misalignment or allow for easy disassembly. The dimensions, materials, and reinforcement of the drive shaft are selected based on the torque, speed, and operating conditions of the machinery.
3. Agriculture and Farming:
Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often requires drive shafts that can handle high torque loads and varying operating angles. These drive shafts are designed to transmit power from the engine to attachments and implements, such as mowers, balers, tillers, and harvesters. They may incorporate telescopic sections to accommodate adjustable lengths, flexible joints to compensate for misalignment during operation, and protective shielding to prevent entanglement with crops or debris.
4. Construction and Heavy Equipment:
Construction and heavy equipment, including excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes, require robust drive shaft designs capable of transmitting power in demanding conditions. These drive shafts often have larger diameters and thicker walls to handle high torque loads. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to accommodate operating angles and absorb shocks and vibrations. Drive shafts in this category may also have additional reinforcements to withstand the harsh environments and heavy-duty applications associated with construction and excavation.
5. Marine and Maritime Applications:
Drive shaft designs for marine applications are specifically engineered to withstand the corrosive effects of seawater and the high torque loads encountered in marine propulsion systems. Marine drive shafts are typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials. They may incorporate flexible couplings or dampening devices to reduce vibration and mitigate the effects of misalignment. The design of marine drive shafts also considers factors such as shaft length, diameter, and support bearings to ensure reliable power transmission in marine vessels.
6. Mining and Extraction Equipment:
In the mining industry, drive shafts are used in heavy machinery and equipment such as mining trucks, excavators, and drilling rigs. These drive shafts need to withstand extremely high torque loads and harsh operating conditions. Drive shaft designs for mining applications often feature larger diameters, thicker walls, and specialized materials such as alloy steel or composite materials. They may incorporate universal joints or CV joints to handle operating angles, and they are designed to be resistant to abrasion and wear.
These examples highlight the variations in drive shaft designs for different types of machinery. The design considerations take into account factors such as power requirements, operating conditions, space constraints, alignment needs, and the specific demands of the machinery or industry. By tailoring the drive shaft design to the unique requirements of each application, optimal power transmission efficiency and reliability can be achieved.


editor by CX 2024-04-25
